Breed Rotational
A three breed rotational uses three breeds of purebred boars, rotated in a consistent order, one breed for each generation. Offspring from each generation are used for market production as well as replacement gilts. Replacement gilts kept from the cross are bred to the breed of purebred boars used least recently
Advantages
- Maintain 86% heterosis in offspring and sows.
- Produce your own replacement gilts.
- System is easy to manage.
- Offspring are uniform as all are genetically the same.
- Most common crossbreeding system.
Disadvantages
Breed composition changes with each generation. If breeds used in the rotation are different in important traits. (i.e. milking ability, growth rate) changes in areas of performance can be different with each generation.
Terminal
In a terminal breeding system, a crossbred gilt (F1) is mated to a terminal purebred boar and all animals are sent to market. Replacement gilts are not kept from this mating and therefore must either be purchased or produced separately. Purebred breeds can be used in a specialized role (i.e. to produce only females or only market hogs) and therefore the strong characteristics of each breed can be fully realized.
Advantages
- Maintain 100% heterosis in both the sows and market animals.
- Can take fulla dvantage of each purebred breeds strengths.
- Uniform market animal as every animal produced is the same genetically.
- System is easy to manage if replacement gilts are purchased and all animals produced go to market
Disadvantages
- If F1 female is purchased, this is an additional cost and disease could possibly be introduced into your herd.
- If F1 female is produced by you, it requires more management as two genetic pools must be maintained, one to produce replacement females and one to produce market animals.
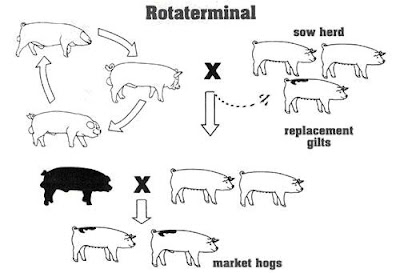
Rotaterminal
Rotaterminal combines the rotational and terminal breeding systems. In a rotaterminal, top females are slected and used in a rotational cross that produces replacement gilts. Maternal breed purebred boards are used in this rotation. The replacement gilts are then mated to terminal boars for market production.
Advantages
- Maintain 86% heterosis in sows and 100% heterosis in market hogs.
- Produce your own replacement gilts.
- Replacement gilts are produced from top sows which means better milking performance.
- Market animals are uniform as all are sired by same breed of boar.
Disadvantages




No comments:
Post a Comment